Functional Food Production Wastewater Treatment
14 Nov, 2025VIET WATER provides complete wastewater treatment solutions for functional food manufacturing plants...
Septic tanks, also known as septic systems, are an essential component in the treatment and disposal of household wastewater, especially in rural areas or places without a centralized sewage system. These systems play a crucial role in treating wastewater from homes before discharging it into the environment. In this article, we will explore what septic tanks are, how they work, their importance, and some maintenance tips for septic tank care.
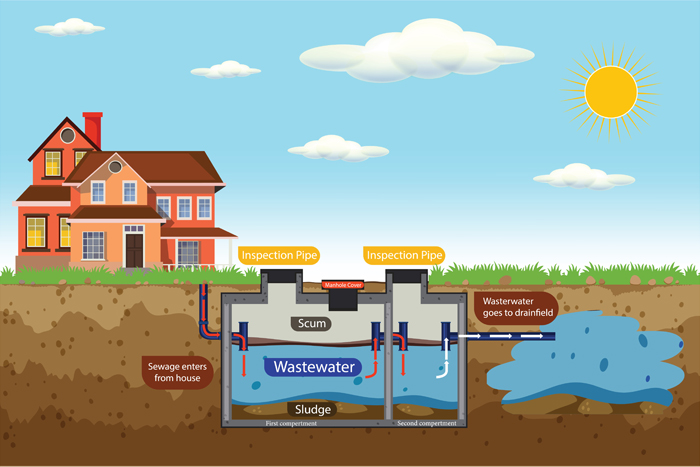
A septic tank is a large underground container designed to collect and treat wastewater from sanitation fixtures such as toilets, sinks, showers, and other domestic wastewater sources. Septic tanks are usually made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic and are typically installed outside the home. The primary purpose of a septic tank is to separate solid waste from liquid waste and treat the wastewater before it is released into the environment.
A septic tank operates based on a natural biological process. When wastewater enters the tank, it separates into three layers:
Bacteria and microorganisms in the septic tank break down and digest the solid waste, converting it into gases and liquid that can be safely absorbed into the ground through the drain field.
Septic tanks play a vital role in wastewater treatment, particularly in areas without centralized sewage systems. Here are some reasons why septic tanks are important:
While septic tanks are highly effective in treating wastewater, they do require proper maintenance to function properly. Some common problems include:
Clogs can occur if non-biodegradable materials such as plastics, grease, or harsh chemicals are flushed down the drain. These materials can interfere with the biological treatment process and cause blockages in the system.
Overflow can happen if the tank is full or if there is a malfunction in the system, causing untreated wastewater to spill over and contaminate the surrounding area.
Foul odors can occur if the tank is not pumped out regularly or if there is excessive scum buildup. Regular maintenance can help prevent this issue.
The drain field can become clogged or damaged if not properly maintained, leading to wastewater backing up into the home or spilling over onto the ground.
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of a septic tank. Here are some maintenance tips:
Septic tanks should be pumped out regularly to remove sludge and scum buildup. Experts recommend having your tank pumped every 3-5 years, depending on tank size and household usage.
Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items like wet wipes, plastics, and harsh chemicals down the toilet or drain. These materials can clog the system and disrupt the treatment process.
Excessive water usage can overload the septic tank and drain field. Repair any leaks and consider using water-saving devices to reduce water consumption.
Regularly inspect the septic tank and its components for any signs of damage, leaks, or other issues. Early detection of problems can help prevent costly repairs.
If you need advice on installing, maintaining, or repairing a septic tank, please contact VIET WATER JSC for professional assistance: